Nighttime leg cramps can be painful and make it hard to sleep. The right sleeping position can lower the chance of these muscle spasms. Lying on your back with a pillow under your knees or on your side with a pillow between your legs helps keep muscles relaxed and improves circulation, which makes cramps less likely. Positions that push the feet downward or curl the legs tightly can make muscles stiff and trigger cramps. Adjusting your position and using pillows to keep your body aligned can keep your legs comfortable through the night.
Besides sleep position, simple changes like stretching before bed, drinking enough water, and managing stress can improve leg comfort at night. These small steps can help you sleep more soundly without interruptions from cramps.
Key Takeaways
- Keeping your legs and spine aligned while sleeping reduces muscle tension.
- Avoid pointing your feet down or tucking your legs too tightly.
- Stretching, hydration, and proper sleep posture can prevent cramping.
- A supportive mattress and using a pillow under or between your knees helps keep the body aligned and lowers the risk of leg cramps at night.
Why Sleep Position Affects Leg Cramps

Sleeping position determines the manner in which muscles relax, circulation, and whether nerves get compressed at night. These factors can make leg cramps more or less likely. Finding a good sleeping position means keeping muscles loose, blood flowing, and nerves free from pressure.
Muscle Contractions During Sleep
Leg cramps happen when muscles tighten on their own and won’t relax. Your muscles normally loosen while you sleep, but certain positions keep some of them tense. For example, pointing your toes down can shorten the calves and make cramps more likely. Positions that let your legs rest naturally help muscles stay loose. Slightly bending the knees toward your chest, like in a gentle fetal position, can relax muscles. Lying flat with straight legs and flexed feet can tighten calves and bring on cramps.
Circulation and Nerve Compression
Blood flow brings oxygen to muscles and carries away waste. Some positions can block circulation or put pressure on nerves, which causes tingling, numbness, or cramps. Sleeping on your side can press on nerves and blood vessels in the hips and legs. That slows circulation and affects how nerves work. Putting a pillow between your legs or placing something under your knees when on your back can reduce pressure and help blood move normally.
Risk Factors for Nighttime Leg Cramps
Dehydration and low electrolytes make muscles more likely to spasm. Overworked muscles from exercise can also tighten up and cramp. Some positions add extra pressure to muscles or nerves. Crossing your legs or curling your toes too tightly increases tension. Pointing your feet down while sleeping also raises cramp risk. Adjusting your position, like using a fetal or straight log position, can ease pressure and help muscles stay relaxed.
Best Sleeping Positions for Leg Cramp Prevention
The correct sleeping positions ensure good circulation of blood and relaxed muscles. Proper support of the legs and prevention of muscle tension can lower the risk of cramps. Minor changes in the way a person sleeps at night can help in comfort and prevention from cramps.
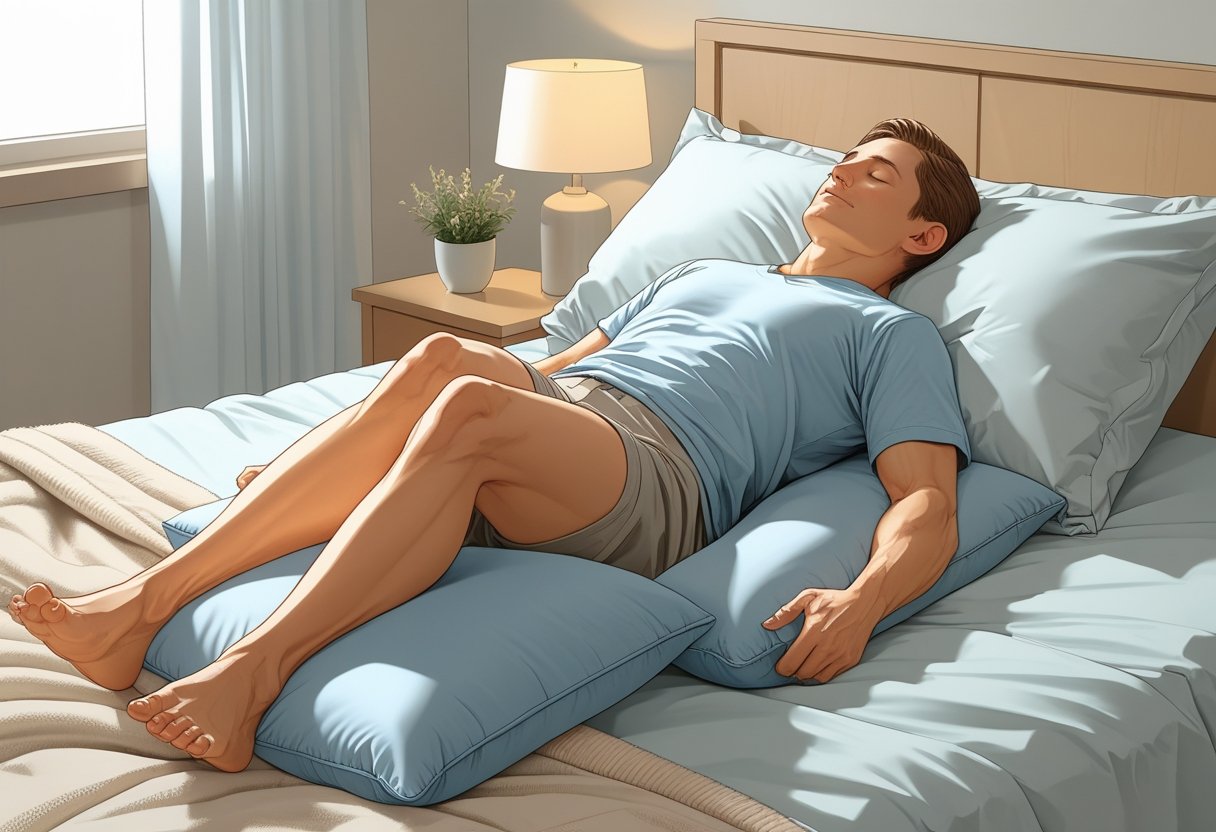
Back Sleeping with Legs Raised
Lying on your back usually helps prevent leg cramps. This position keeps your spine and legs in a neutral line, reducing pressure on muscles and nerves. Placing a pillow under your knees creates a gentle curve that relaxes the calf muscles. Raising your legs slightly with a pillow or a rolled towel also improves blood flow. This helps avoid muscle strain and keeps circulation even in your lower body. It also stops your toes from pointing down, which can tighten the calves and cause cramps.
Side Sleeping with Proper Support
Side sleeping can work well if you support your legs correctly. Bending your knees and hips a little keeps your spine straight and lowers muscle tension. Putting a pillow between your knees prevents the top leg from pulling on the bottom one, easing pressure on hips and thighs. This position helps align the legs and reduces areas of high pressure. It also avoids restricting blood flow from legs being pressed together. People who often get leg cramps may find this position comfortable and relaxing.
Fetal Position for Muscle Relaxation
The fetal position, with knees drawn toward the chest, can help muscles relax. It opens the hips and eases tension in the legs. But curling too tightly can block circulation, so keep a gentle curve. Adding a pillow behind your back or between your legs helps maintain alignment and keeps muscles loose. This can prevent cramps caused by nerve pressure or overworked muscles. Many people feel relief in this position because it supports a natural resting posture for the legs.
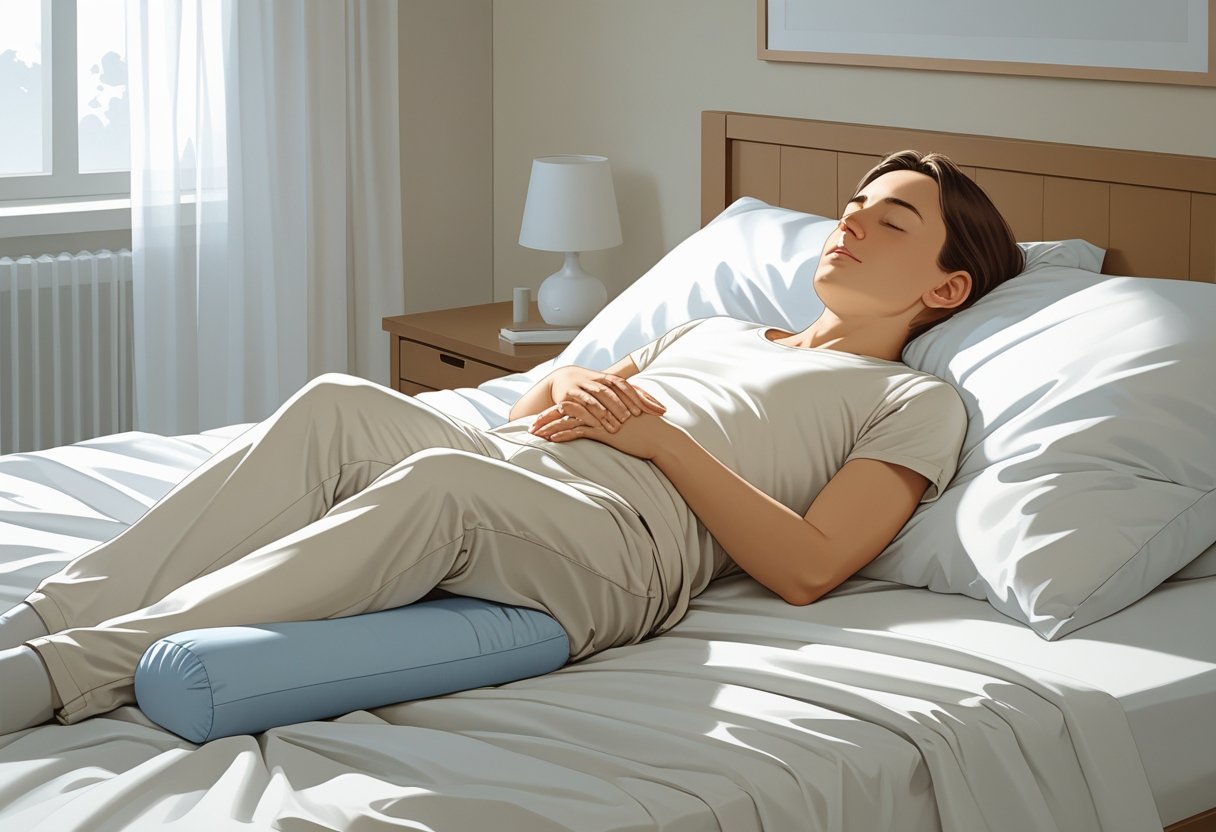

Optimizing Your Sleeping Position
Choosing the proper sleeping position will help relax muscle tension and circulate blood in the legs. Minor changes can lower the risk of cramps by stabilizing muscles and maintaining joints in a relaxed position. Proper support of the legs, position of the feet, and spinal and hip alignment all have a significant impact.
Utilizing Pillows to Support Legs
Pillows can help keep the legs relaxed while sleeping. If you sleep on your back, placing a pillow under the knees slightly bends them. This eases pressure on the calf muscles and improves blood flow.
For side sleepers, putting a pillow between the knees stops the top leg from pulling on the hip. This keeps the hips aligned and reduces strain on muscles. It also prevents the legs from twisting or crossing, which can affect circulation and cause cramps. Using pillows like this keeps muscles relaxed and lowers the chance of waking up from sudden cramps. The goal is to find pillow positions that feel natural and comfortable without forcing the legs into awkward angles.
Maintaining Neutral Foot Position
Keeping the feet in a neutral position helps prevent cramps. Pointing toes down, called plantar flexion, tightens the calf muscles and can lead to cramping. Feet should rest naturally, either flat or slightly flexed toward the shin (dorsiflexion). This reduces tension in the calves and encourages blood flow.
People who often get leg cramps should avoid positions that force the feet downward, like sleeping on the stomach with stretched-out feet. Using foot rolls or small supports can help keep the feet neutral through the night.
Alignment of Spine and Hips
Spine and hip alignment matters for relaxed leg muscles. When the body is aligned, nerves and blood vessels in the legs aren’t compressed or irritated.
Back sleepers benefit from a pillow under the knees. It keeps the natural curve of the spine and aligns the hips, which lowers muscle tension that can cause cramps. Side sleepers should keep their legs slightly bent and hips stacked. A pillow between the knees prevents the lower leg from twisting and protects nerves from pressure. Keeping the spine and hips aligned supports healthy muscles and reduces the risk of painful leg cramps at night.
Positions and Habits to Avoid
Some sleeping patterns and positions themselves can cause muscle tension and decrease blood flow, so it’s more likely to get a leg cramp. Avoiding them can assist in relaxing leg muscles and ensuring that blood flow is improved during sleep.
Stomach Sleeping and Toe Pointing
Sleeping on your stomach usually makes your feet point downward, which is called plantar flexion. This tightens the calf muscles and can make leg cramps more likely. Stretching your legs out flat can also put strain on muscles and nerves. This may lead to cramps at night that are more frequent and stronger. You can reduce the risk by avoiding stomach sleeping. If you must sleep that way, putting a pillow under your hips helps reduce pressure and stops your ankles from pointing down too far.
Crossed Legs and Over-Flexion
Crossing your legs in bed can limit blood flow and pinch nerves. This can weaken muscles and raise the chance of cramps. Curling up tightly in a fetal position also bends your knees and hips too much. That can reduce circulation and add stress to your leg muscles. Using pillows for support can help. Keeping your legs slightly bent and relaxed with some space lets blood flow properly and lowers the risk of cramps.

Additional Nighttime Strategies to Prevent Leg Cramps

Basic pre-bedtime habits can minimize the risk of leg cramps. Priming muscles with stretches and maintaining body fluid levels and balance of electrolytes are important steps.
Stretching Before Bed
Stretching targets muscles that often cramp, like calves, hamstrings, and quadriceps. Stretching the calves helps release tension in the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles, letting them relax and lowering the chance of cramps at night. Hold each stretch for 15 to 30 seconds without bouncing. Stretching too hard can cause injury or make cramps worse. Doing these stretches every day before bed improves flexibility and lowers cramp risk.
Adding stretching to an evening routine signals the body to relax. It can improve muscle tone and prevent sudden contractions. Skipping stretches can make cramps more likely.
Hydration and Electrolyte Balance
Staying hydrated helps muscles work well and prevents spasms. Drinking water during the day, especially after exercise or heat exposure, is important.
Electrolytes like potassium, magnesium, and calcium control muscle contractions and nerve signals. Low levels can trigger cramps. Eating foods such as bananas, nuts, leafy greens, and dairy supplies these minerals naturally. Try to limit fluids right before bed to avoid waking up at night. People with frequent cramps may need electrolyte supplements, but only if a doctor recommends them.
Together, proper hydration and balanced electrolytes help muscles stay stable and reduce the chance of leg cramps at night.
When to Seek Further Help for Persistent Leg Cramps
Chronic leg cramps that interfere with sleep or daily life might require medical care. If cramps happen a lot or are very painful, it is best to see a doctor.
Indications that need further examination include:
- Leg swelling, redness, or heat
- Muscle weakness or shrinking
- Cramps with numbness or tingling
- Pain that shows up mainly during exercise
These symptoms could point to issues like poor circulation, nerve compression, or other health problems. A doctor will ask about how often the cramps happen, how long they last, and how severe they feel. They may also suggest tests to check for electrolyte imbalances, thyroid problems, or vascular conditions.
Choosing the Right Mattress and Position to Ease Leg Cramps
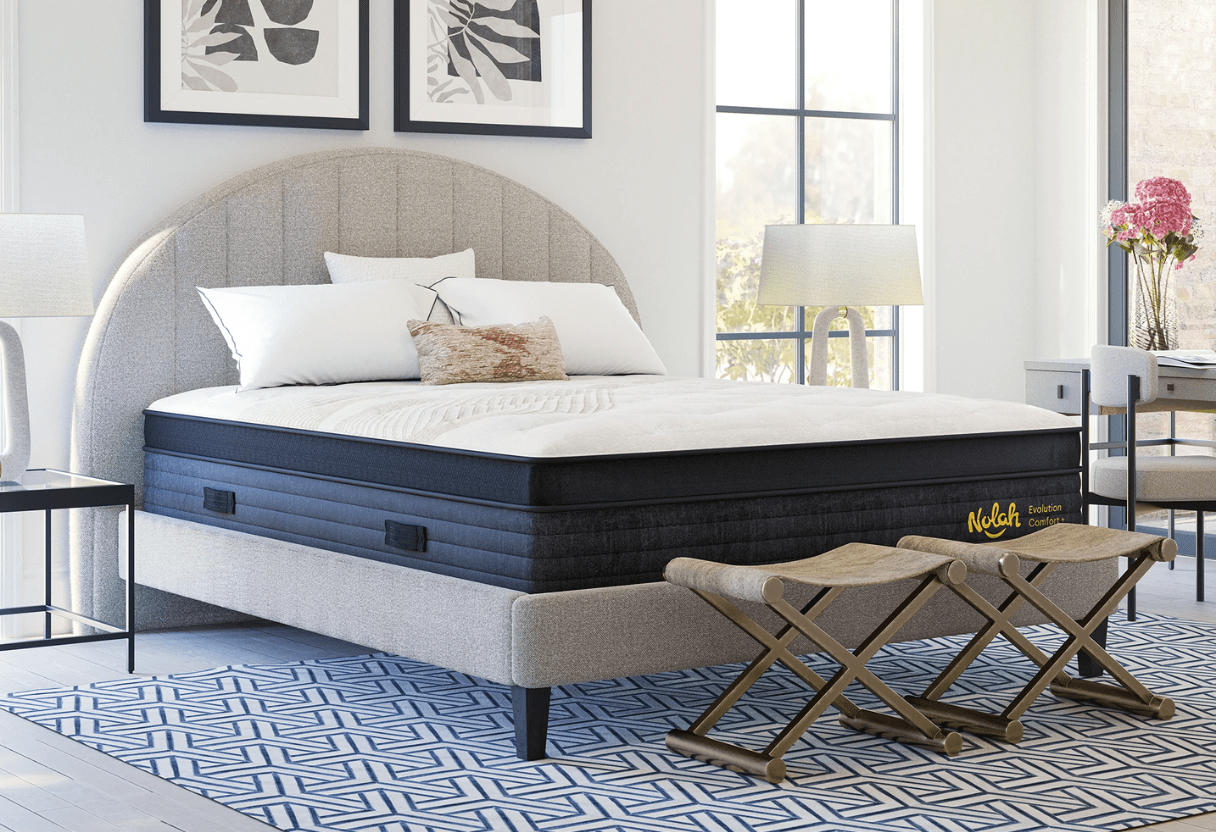
Your mattress affects how your body rests and can help with leg cramps. If it’s too soft or too firm, certain points on your body press too hard. This can slow blood flow and tighten muscles, which may lead to cramps. Memory foam or latex mattresses are good at easing leg cramps. They bend to your body and spread weight evenly. That way, your legs don’t take all the pressure, and muscles stay looser while you sleep.
How you sleep matters too. Lying on your back with a pillow under your knees bends your legs just a little and relaxes calf muscles. Side sleepers can put a pillow between their knees to stop the top leg from pulling on the bottom. This keeps muscles and nerves calm.
Try not to sleep with toes pointed down or legs sharply crossed. These positions make calves tense and limit blood flow, which can cause cramps.
Strategic use of pillows enhances comfort and support:
- Back sleepers: A pillow under the knees keeps legs bent and circulation smooth.
- Side sleepers: A pillow between the knees aligns hips and lowers muscle strain.
Choosing a mattress and position that fits together helps muscles relax and blood move freely. The Nolah Evolution Comfort+ Mattress, for example, has supportive foam and zoned coils. It holds heavier parts like hips and shoulders while supporting legs gently. This can reduce pressure points and keep circulation steady through the night.

Frequently Asked Questions
Some sleep positions, eating habits, and lifestyle choices can trigger leg cramps at night. Understanding what helps your body can reduce them.







